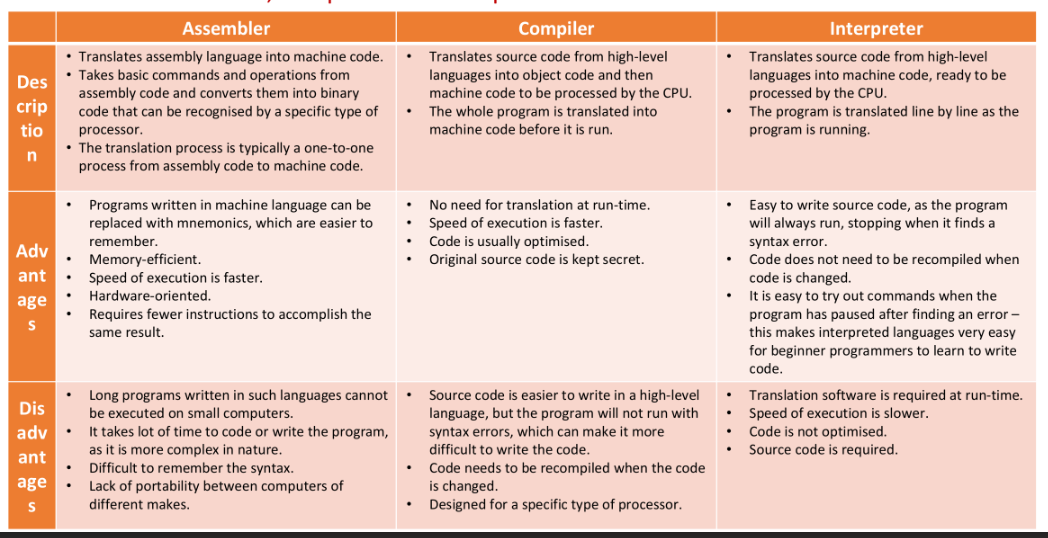
Translators are programs which convert program source code from a high-level langauge to a low-level language.
There are three types:
- Assemblers
- Compilers
- Interpreters
Assemblers
Assemblers translate assembly language into machine code.
Info
As assembly is 1:1 with binary code, it is fully reversable, unlike compilers and interpreters.
Example: NASM (Netwide Assembler), MASM (Microsoft Macro Assembler)
Compilers
Compilers translate the entirety of source code into machine code.
Programs which are compiled have better performance than interpreters as there is it is not performed during runtime, but this means that debugging can be more challenging as initial compiling may take long amounts of time.
Example: GCC (GNU Compiler Collection), Clang (LLVM frontend), MSVC (Microsoft Visual C compiler)
In-depth: Compilers
Interpreters
Interpreters interpret the source code line-by-line and then execute them, being performed at runtime.
They are much slower due to this step being performed before each ‘instruction’, but is easier to debug as it is generally much faster to start, coinciding more detailed error messages.
Comparison